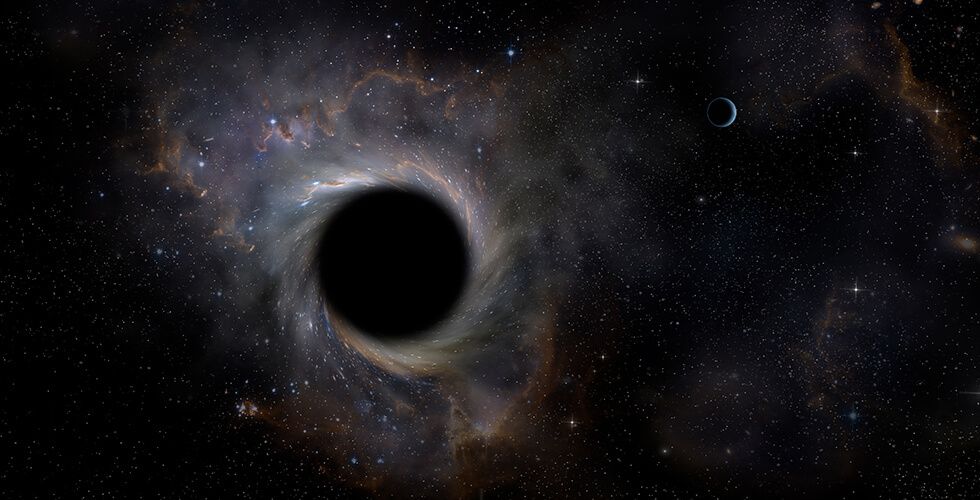
For the first time in history, astronomers have confirmed the existence of a black hole wandering alone through the galaxy, unattached to any star, planet, or system. This incredible discovery marks a cosmic milestone and could unlock a whole new class of elusive celestial objects.
The journey to this breakthrough began years ago when researchers spotted a strange, invisible “dark object” moving through the constellation Sagittarius. Some believed it to be a rogue black hole; others argued it was likely a neutron star. The debate raged on—until now.
Thanks to fresh data from the Hubble Space Telescope (2021–2022) and the Gaia space observatory, scientists have gathered enough evidence to tip the scale. The object weighs in at around seven times the mass of our sun—too heavy to be a neutron star, which means one thing: it’s a black hole.
What makes this detection so rare? Most black holes reveal themselves by interacting with nearby stars, pulling material into their gravitational grip. But this one was invisible—until it briefly passed in front of a distant star and caused its light to bend and brighten in a phenomenon called gravitational microlensing.
The black hole, which has no companion and no visible light, is now officially the first “rogue” black hole ever confirmed. Even the rival research group, which initially questioned the claim, has since changed its stance, publishing an updated analysis in 2023 and agreeing with the findings.
Scientists hope this is just the beginning. With the launch of NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope in 2027, we may soon uncover many more of these stealthy, wandering giants, proving that even in the vast silence of space, the universe is full of invisible marvels waiting to be seen.